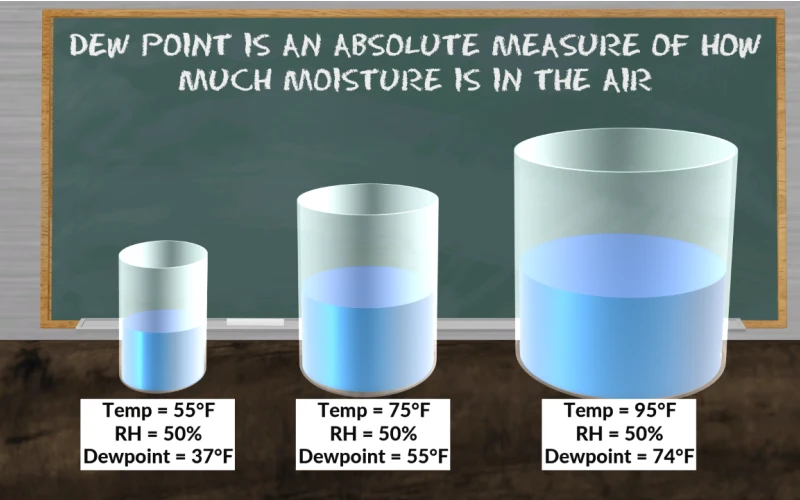
,字数在1000字左右
# How is Dew Point Calculated?
Dew point is a crucial meteorological parameter that indicates the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, frost, or fog. Understanding how dew point is calculated is essential for weather forecasting, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes. In this article, we’ll explore the science behind dew point calculation and the methods used to determine it.
## The Science Behind Dew Point
Dew point is directly related to the amount of water vapor present in the air. When air cools to its dew point temperature, it reaches 100% relative humidity, meaning it can no longer hold all of its water vapor. The excess water vapor then condenses into liquid water or deposits as frost if the temperature is below freezing.
The relationship between dew point, temperature, and humidity is governed by the principles of thermodynamics and the properties of water vapor in air. The calculation of dew point involves understanding these relationships and applying appropriate formulas or using psychrometric charts.
## Basic Formula for Dew Point Calculation
The simplest approximation for dew point calculation is the Magnus formula:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
– Td is the dew point temperature
– T is the air temperature
– RH is the relative humidity
– a and b are constants (a = 17.27, b = 237.7°C)
– α(T,RH) = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH/100)
This formula provides a good approximation for temperatures between 0°C and 60°C.
## Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Let’s break down the calculation process:
1. Convert temperature to Celsius if necessary
2. Calculate the intermediate variable γ:
γ = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH/100)
3. Calculate dew point:
Td = (b × γ)/(a – γ)
For example, for air at 25°C with 50% relative humidity:
γ = (17.27 × 25)/(237.7 + 25) + ln(0.5) ≈ 1.646 – 0.693 ≈ 0.953
Td = (237.7 × 0.953)/(17.27 – 0.953) ≈ 226.5/16.317 ≈ 13.88°C
## More Accurate Calculation Methods
For greater precision, especially in scientific and industrial applications, more complex equations are used:
### The August-Roche-Magnus Approximation
This enhanced version provides better accuracy across a wider temperature range:
Td = (c × ln(RH/100) + (d × T)/(e + T)) / (f – ln(RH/100) – (g × T)/(e + T))
Where c, d, e, f, and g are empirically determined constants.
### The Arden Buck Equation
This is one of the most accurate formulas, especially for high temperatures:
Td = (c × ln(RH/100) + (d × T)/(e + T)) / (f – ln(RH/100) – (g × T)/(e + T))
Where the constants vary slightly depending on the temperature range.
## Practical Methods for Determining Dew Point
In addition to mathematical calculations, there are practical ways to determine dew point:
### Psychrometric Charts
These graphical tools allow users to find dew point by plotting known values of temperature and relative humidity. The intersection point reveals the dew point temperature.
### Dew Point Meters
Modern instruments called dew point meters or hygrometers measure dew point directly using various technologies:
– Chilled mirror hygrometers
– Capacitive sensors
– Resistive sensors
– Optical sensors
### Online Calculators and Apps
Numerous digital tools are available that perform dew point calculations
Keyword: how is dew point calculated